Mohamad-Ali Salloum is a Pharmacist and science writer. He loves simplifying science to the general public and healthcare students through words and illustrations. When he's not working, you can usually find him in the gym, reading a book, or learning a new skill.
What is the next step?
Share
We are humans, and we are programmed to always think in advance to predict what is coming next and try to survive and make it more meaningful (1) (2). That’s how we evolved through history.
In the modern days, and with the enormous loads of data that are generated daily, our brains can’t handle any more input so we can assess the situation and decide upon it.
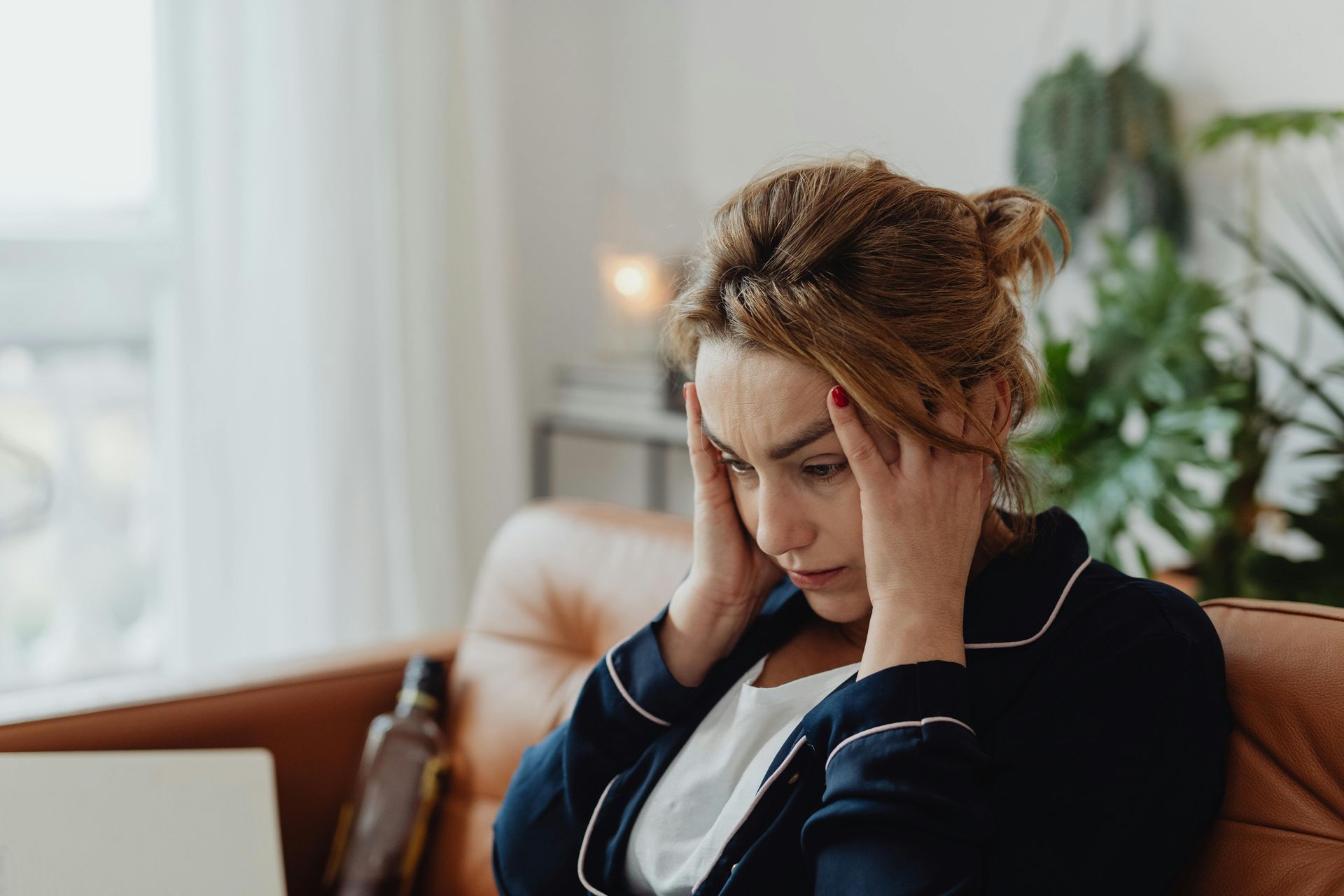
And that’s where we become overwhelmed.
The technologies we are using evolved faster than our brains are. Our brains are used to counting simple numbers, now we are trying to assess situations based on a huge amount of data that we have collected.
Let’s take an example.
A teenager enters the phase of trying to decide what he wants to do for the rest of his life as a career. Of course, his parents and surroundings will have a big impact on his decision. If he is stubborn enough, he will be able to make his own decision. He tries to see what he likes and what the earlier people in this field have done, what are the future expectations for this career?
Is it going to be replaced by robots?
Will this job role be extinct in the next few years?
What if I was 40 years old and I got fired?
A lot of questions will go through his mind.
Then he searches for his other career options and faces the same dilemmas and dead-end questions.
Once all the data accumulate in his still-developing brain, he will feel helpless in front of all the data he collected and not know what to decide. This usually happens to humans when we feel that we have no control over what we want to do. This often leads to procrastination, frustration, burn-out, having no life goals in the long-term, depression, and anxiety.
There are several ways to handle this situation. Let me walk you through them.
1) Draw all your thoughts in front of you.
Categorize your thoughts and fill the correct thoughts in their respective categories. For example, in the obstacles category, put all the obstacles you thought about. Your categories should also include solutions, people that might help, and mentors in the career that will be able to enlighten you...don’t hold any thought in your brain, write all of them down no matter how they seemed extreme.
2) Start connecting the points you’ve written and draw maps on how to proceed.
Draw maps connecting the obstacles with their respective solutions and a list of people or things that might help to solve the obstacle.
3) Once you connect all the points and finish the map, you will already have a plan now.
Make your plan clean and write it in a clearer way.
4) Cut down your plan into smaller tasks and estimate how much time and money it will cost you.
Once you cut down your plan into small chunks, even rocket science will seem simple. Start practicing this habit.
5) Start acting on it.
All of the mentioned steps before will not make you accomplish what you want unless you actually start doing.
Congrats, you saved yourself from being overwhelmed and stuck in the same place.
If you tried to do the above steps and did not know how to proceed or was stuck at a point, ask for help. A lot of people are out there to help you when you ask for it. They will not be able to know that you need help if you did not say that clearly.
This plan applies to all fields of life: school, universities, work, relationships….
Goodluck in excelling at your lives :)
List of Services
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Mohamad-Ali Salloum, PharmD
Share
Recent articles: